Understanding the Digital Markets Act (DMA)
- ISE Mallorca
- 20.12.2024 г.
- време за четене: 2 мин.
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is a groundbreaking EU regulation aimed at creating fairer and more contestable markets in the digital sector. It targets the largest digital platforms, or "gatekeepers," and establishes specific obligations and prohibitions to regulate their operations. Here's what you need to know:

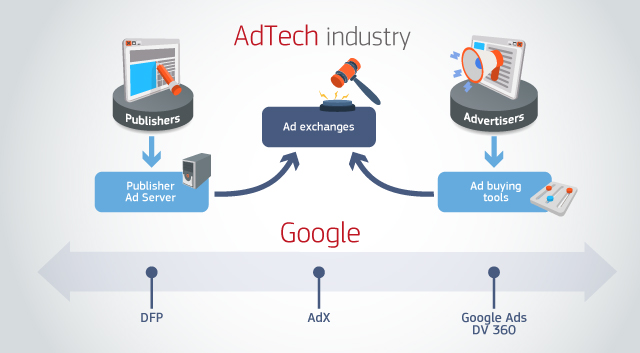
What is the DMA About?
The DMA sets objective criteria to identify gatekeepers—large digital platforms providing key services such as online search engines, app stores, and messaging services. These platforms are required to comply with "do’s" (obligations) and "don’ts" (prohibitions) to ensure fairness in the digital market.
The DMA complements EU competition laws but does not replace them.
Legislative Timeline
Proposal: December 2020 by the European Commission.
Adoption: 14 September 2022 by the European Parliament and the Council.
Entry into Force: 1 November 2022.
Applicability: 2 May 2023.
Companies meeting the thresholds for core platform services must notify the Commission, which will designate gatekeepers and monitor compliance.
Key Rules for Gatekeepers
Obligations ("Do’s")Gatekeepers must:
Allow third-party interoperability in certain situations.
Enable business users to access data generated through the platform.
Provide advertisers with tools for independent ad verification.
Allow businesses to promote and conclude deals outside the gatekeeper's platform.
Prohibitions ("Don’ts")Gatekeepers cannot:
Favor their own products or services in rankings over third-party offerings.
Block consumers from connecting with businesses outside their platform.
Prevent users from uninstalling pre-installed apps or software.
Track users for targeted advertising without explicit consent.
Benefits for Consumers and Businesses
For Consumers: Greater choice, transparency, and control over services and data.
For Businesses: Fairer competition and access to tools for verifying advertisements and promoting products independently.
Adapting to a Dynamic Digital Sector
The European Commission will conduct market investigations to:
Identify new gatekeepers.
Dynamically update obligations.
Design remedies for systematic rule violations.
Non-Compliance Consequences
Fines: Up to 10% of global annual turnover (20% for repeated infringements).
Penalty Payments: Up to 5% of daily turnover.
Remedies: Behavioral or structural actions, including divestiture of parts of a business, for systematic violations.
The Digital Markets Act represents a significant step toward fostering a fair and competitive digital economy in the EU. It ensures that large platforms operate transparently and fairly, benefiting consumers, businesses, and the broader market. For further details, visit the European Commission's official resources.



Коментари